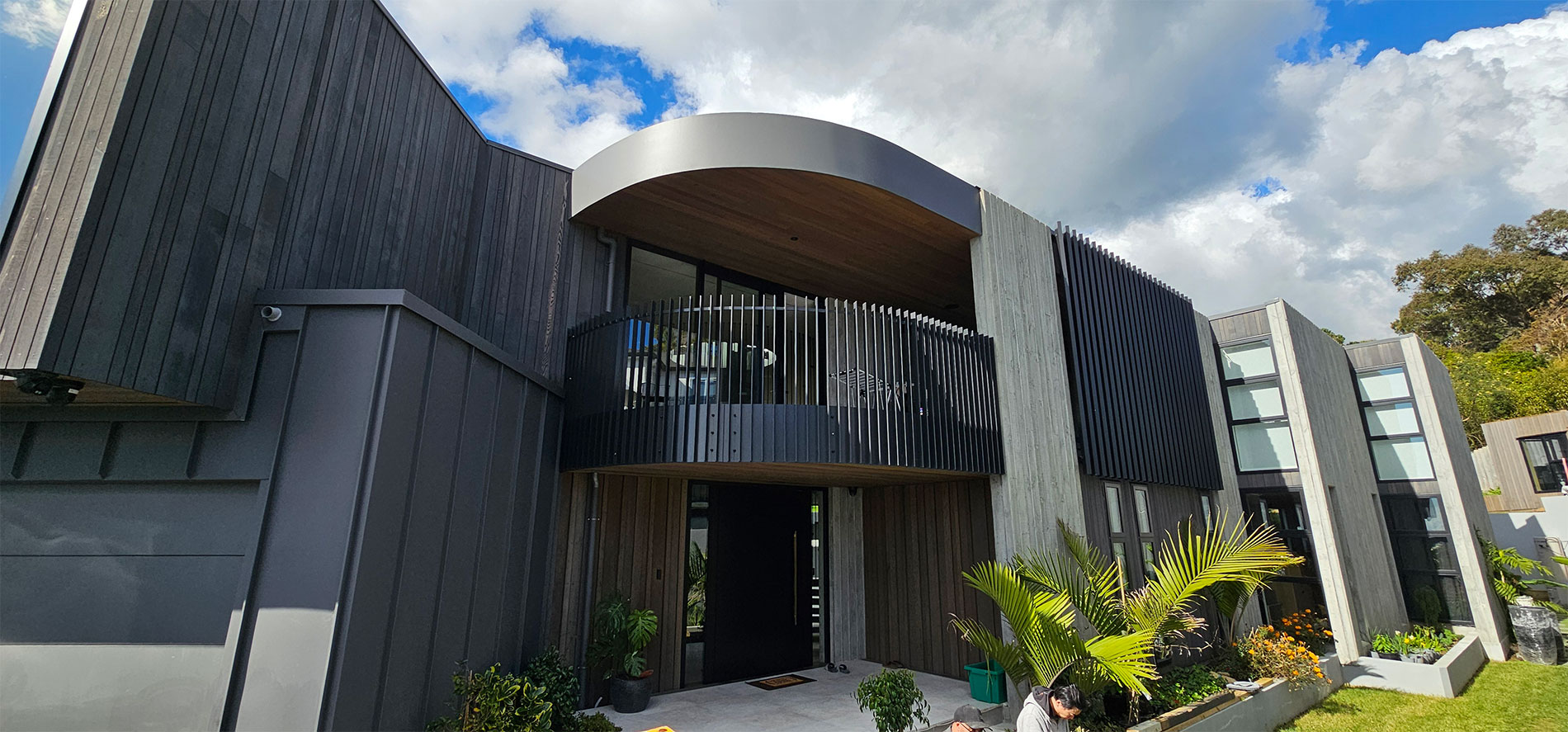
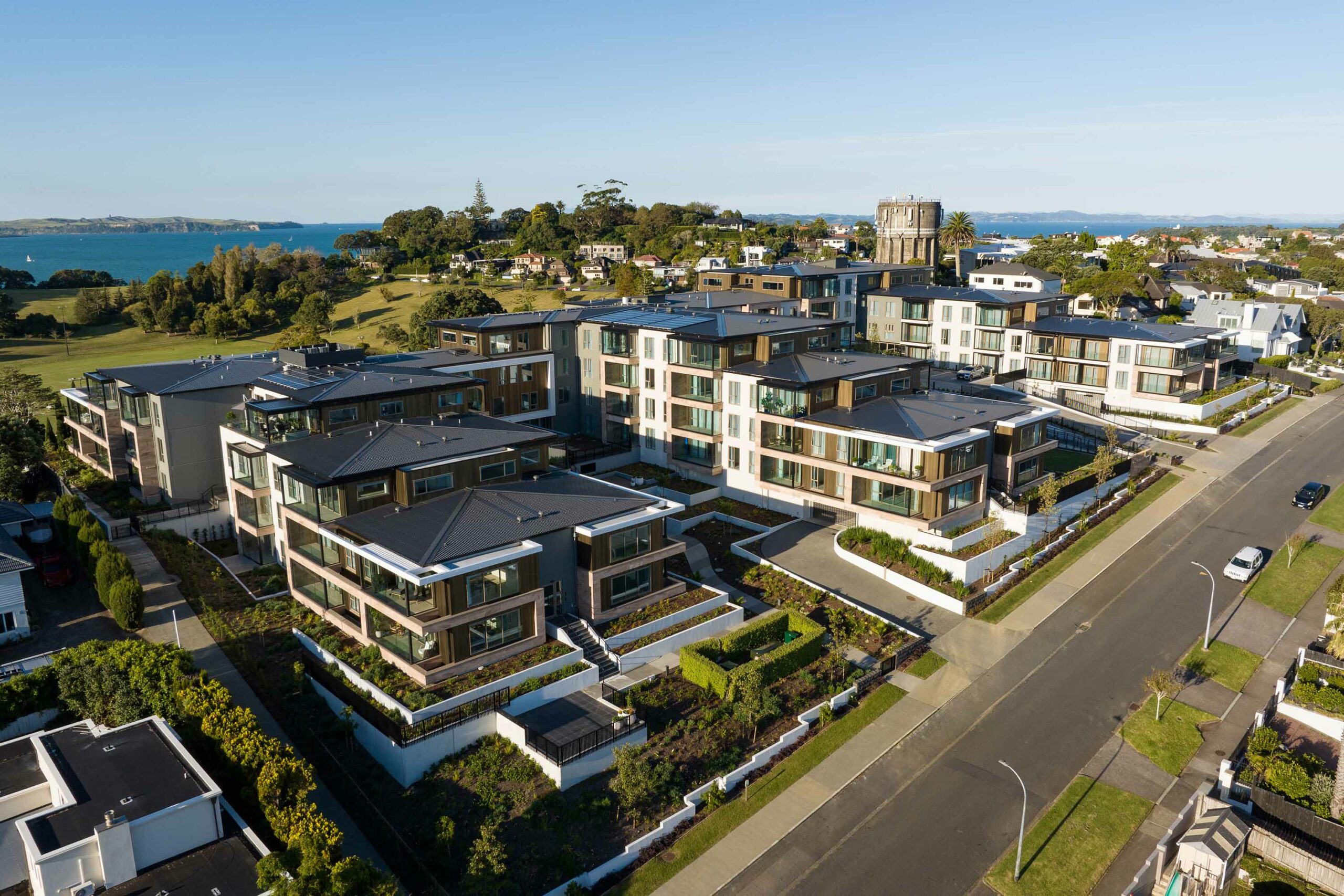
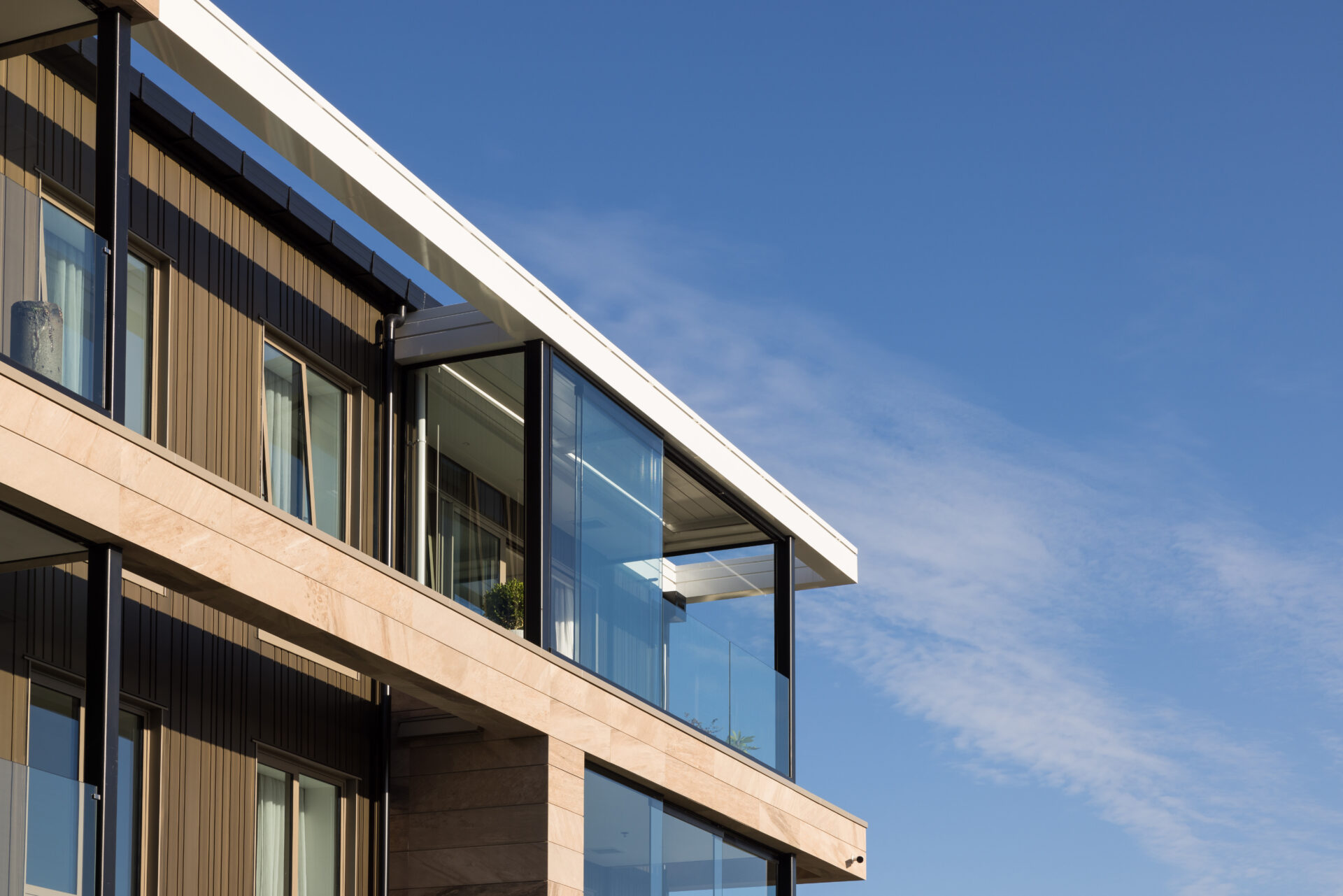
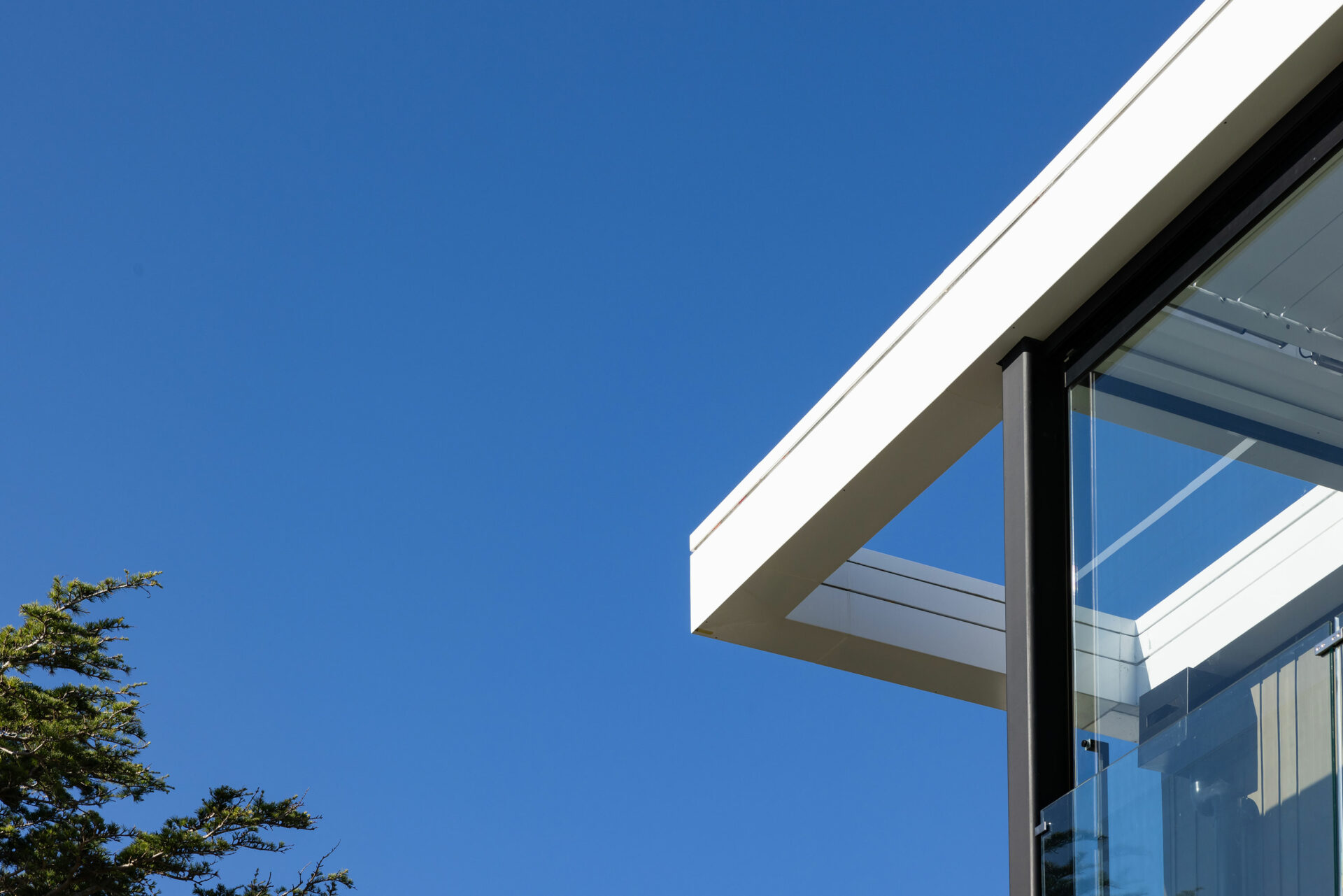
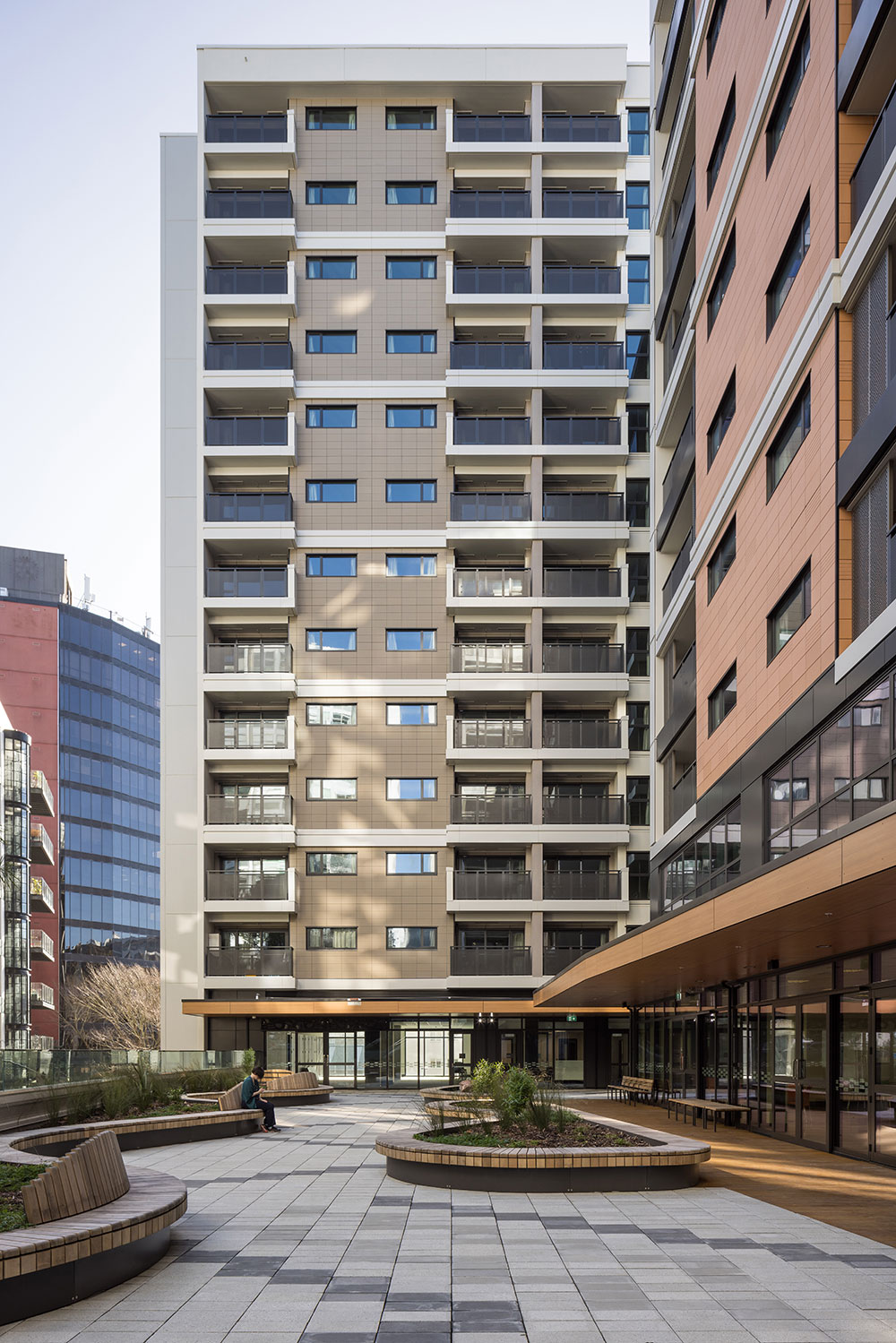
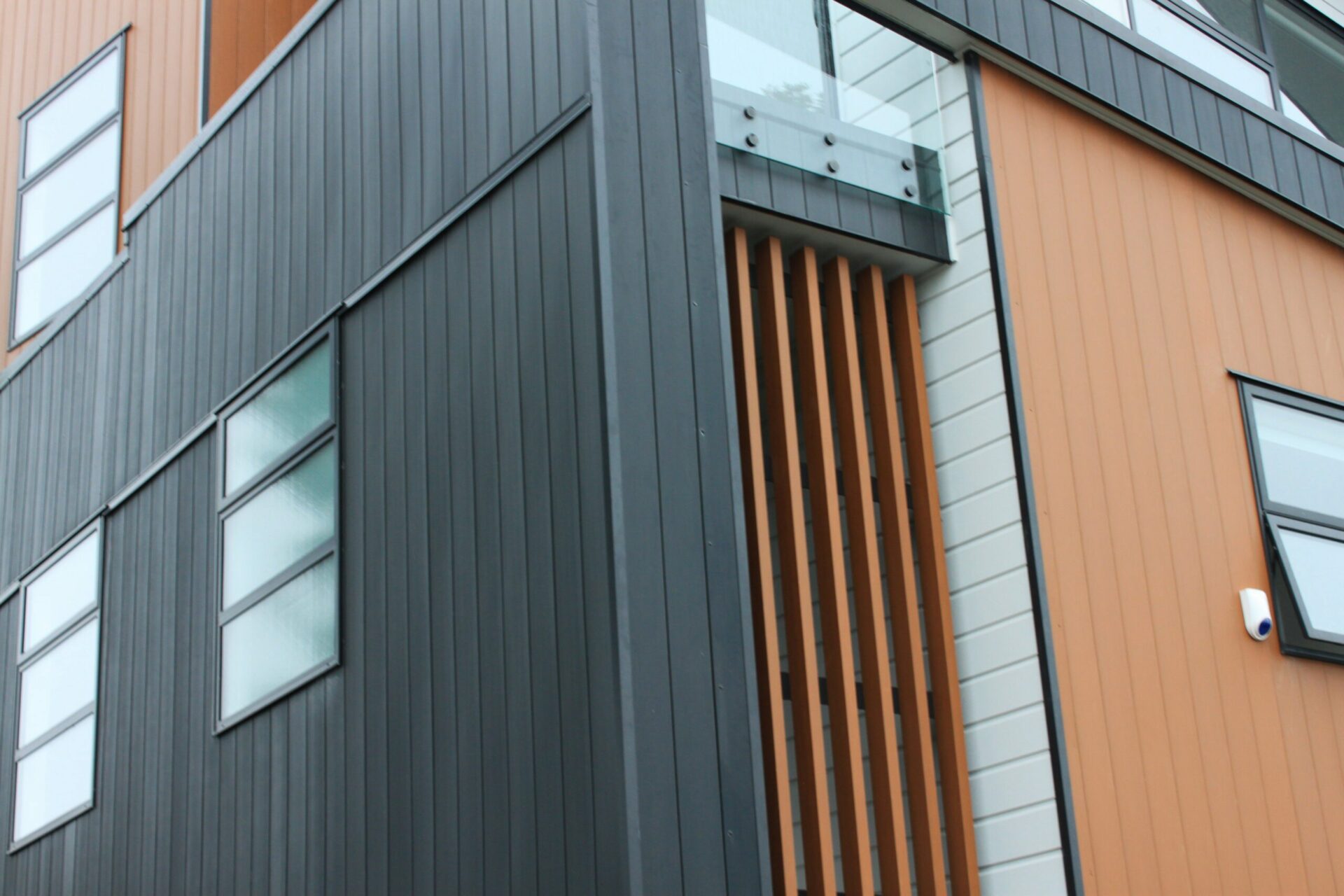
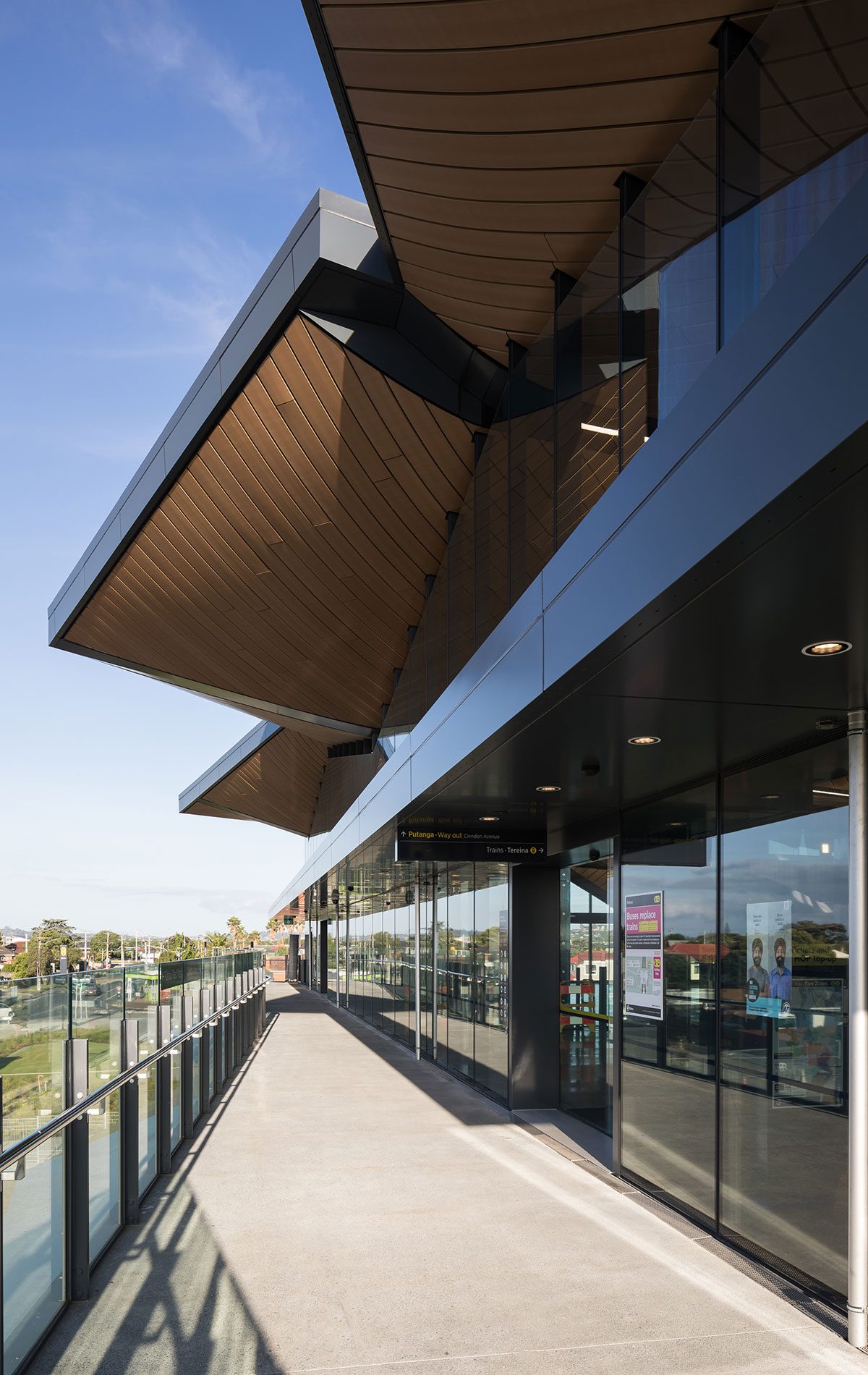
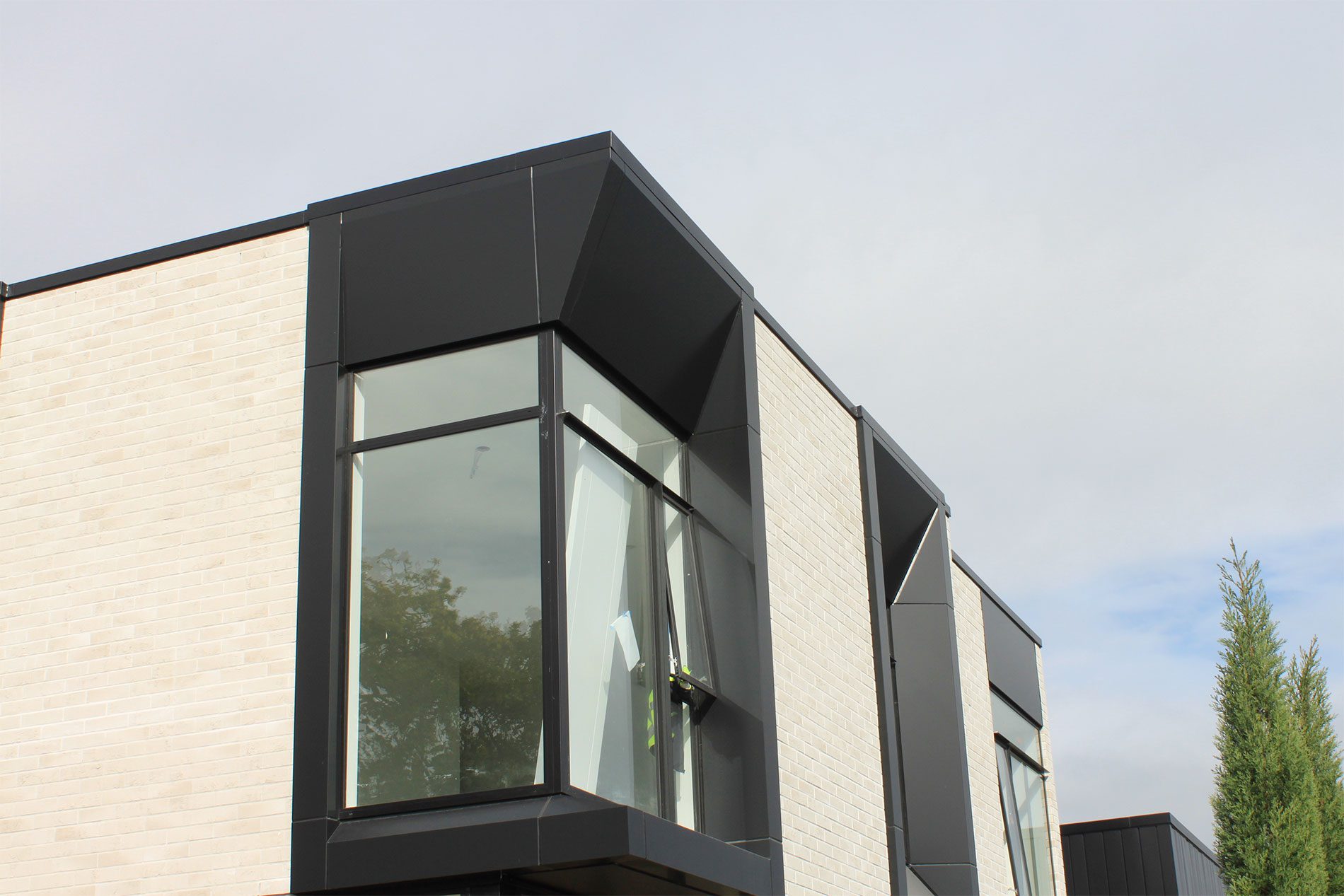
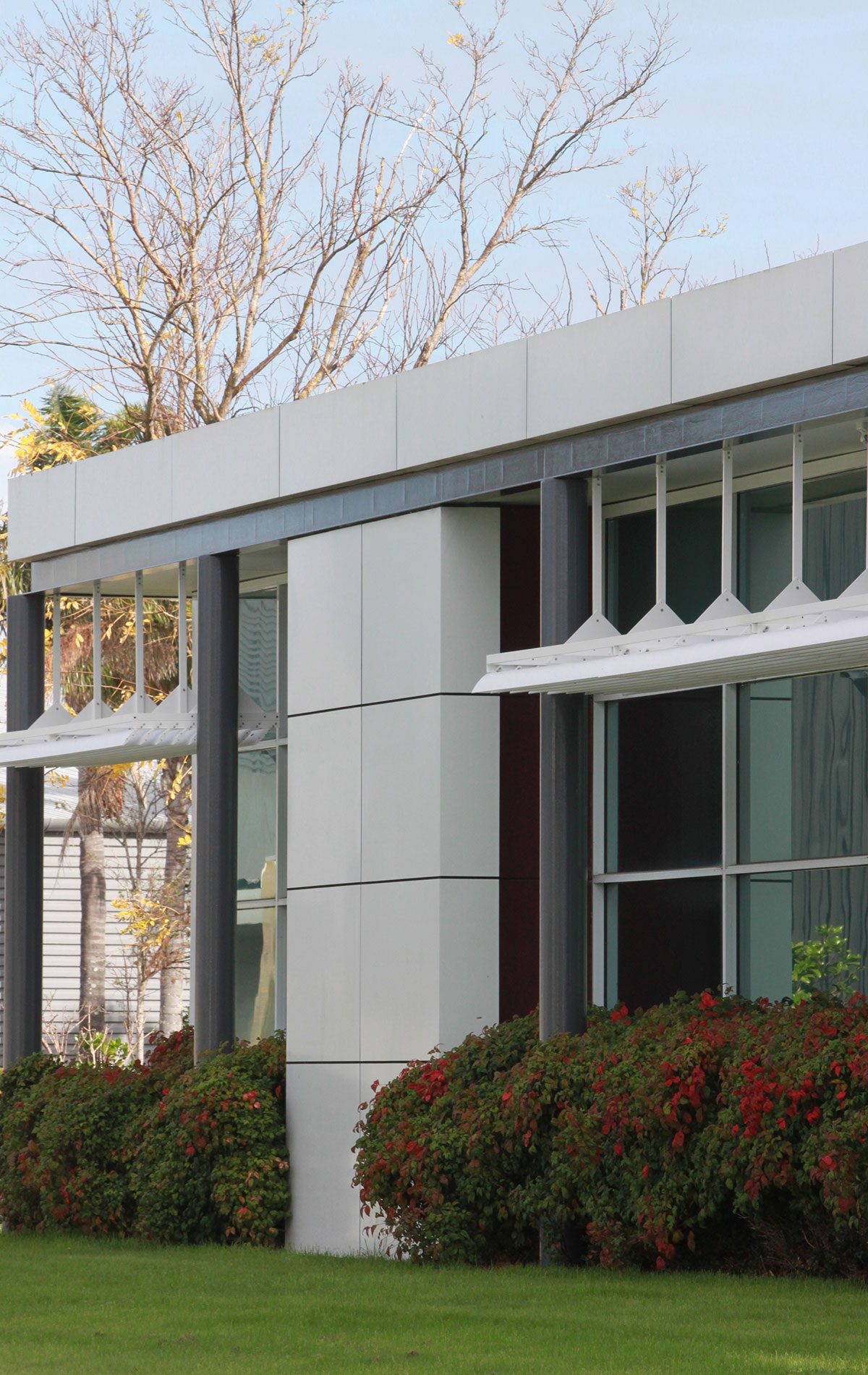
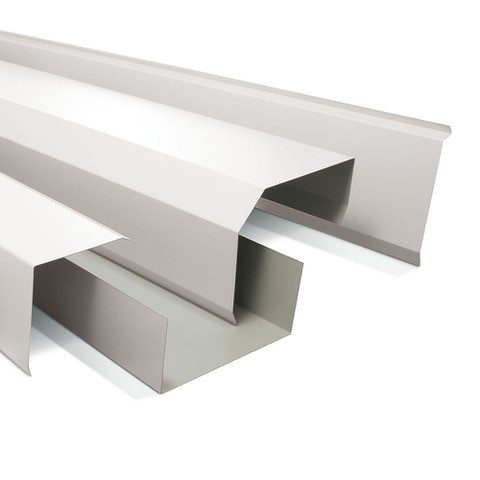
Flashings are a critical component of the weathertightness of a building, whether protecting the head of a window or a roof cladding junction.
Flashings play a vital role in preventing external moisture from getting through the building envelope (called primary defence) and ensuring that any moisture that does get in can drain out again (called secondary defence). Flashings are defined in New Zealand Building Code clause E2 External moisture as ‘component[s] formed from a rigid or flexible waterproof material that drains or deflects water back outside the cladding system’.
Flashings are typically required at:
- roof junctions and edges such as barges and gutters
- changes in roof pitch such as ridges and hips
- roof and wall penetrations such as windows, doors, meter boxes, skylights, flues and pipes
- roof/wall intersections such as soffits, parapets and balustrades
- vertical and horizontal junctions between cladding materials
- intersections between different building elements.
Flashings must meet the requirements of Building Code clauses:
- B2 Durability
- E2 External moisture